Many institutional and retail investors are growing interest in Decentralized Finance (DeFi) because of the increase in liquidity and number of users. There are certain terms that are key to decentralized exchanges and Automated market maker (AMM) is one of them. In this article, we will go through what AMM is and how it works with an example.
What is Automated Market Maker?
Automated Market Maker (AMM) is a part of the Decentralized Finance (DeFi) ecosystem. Its purpose is to create a decentralized exchange market. In traditional finance, the market is created with the help of order books. An order book is basically a list of buyers and sellers for a specific financial instrument. This is an example of a simple order book on Binance exchange.
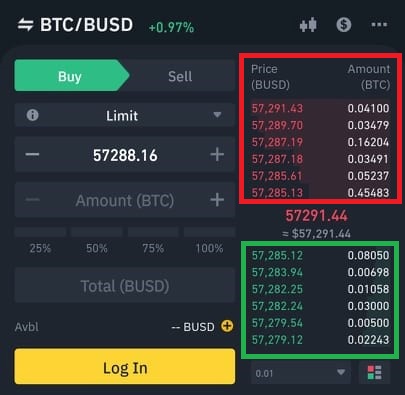
Marked red are the sell orders and marked green are the buy orders for pair BTC/BUSD. In traditional finance, there is a buyer and seller between whom is a central exchange in order for a trade to take place. However, in decentralized exchanges, there is no need for a second party because an automated market maker mediates trade between buyer/seller and contract taken from the liquidity pool.
Automated market makers replace traditional order books with a simple algorithm. That algorithm, which uses a smart contract, controls price changes in a liquidity pool. Simply said, automated market makers enable automated and decentralized trading for the market.
Automated market maker was first utilized on Uniswap in 2018.
How Does Automated Market Maker Work?
Automated market maker works using the XYK model which represents the simple mathematical formula X*Y=k. X and Y are amounts of assets in the liquidity pool, and k represents the constant amount of liquidity in the pool.
For easier understanding, I will give an example. Let’s say we have two cryptocurrencies, A and B. We create a liquidity pool from that A/B pair in a 1:1 ratio with 5 of each. In that case, the total liquidity pool would equal 25 (5×5). The buyer steps in and wants to buy 1 A with his 1 B. So now we have 6 B in the liquidity pool, but the constant (k) amount must remain the same and that is where AMM comes to play. AMM’s algorithm subtracts A amount (5) by the divided constant (k) amount (25) from B amount (6). And the buyer gets 0.83 of A for the amount of 1 B.
Which Are The Most Known Automated Market Maker Protocols?
The first and most used protocol that utilized automated market maker is Uniswap. It runs on the Ethereum blockchain and users can swap tokens automatically and without permission. In addition to that, anyone can lend their crypto to earn fees. Alongside Uniswap, Curve and Balancer are some of the popular AMM protocols.